HMI Builder allows the rapid creation of Operator Interfaces.
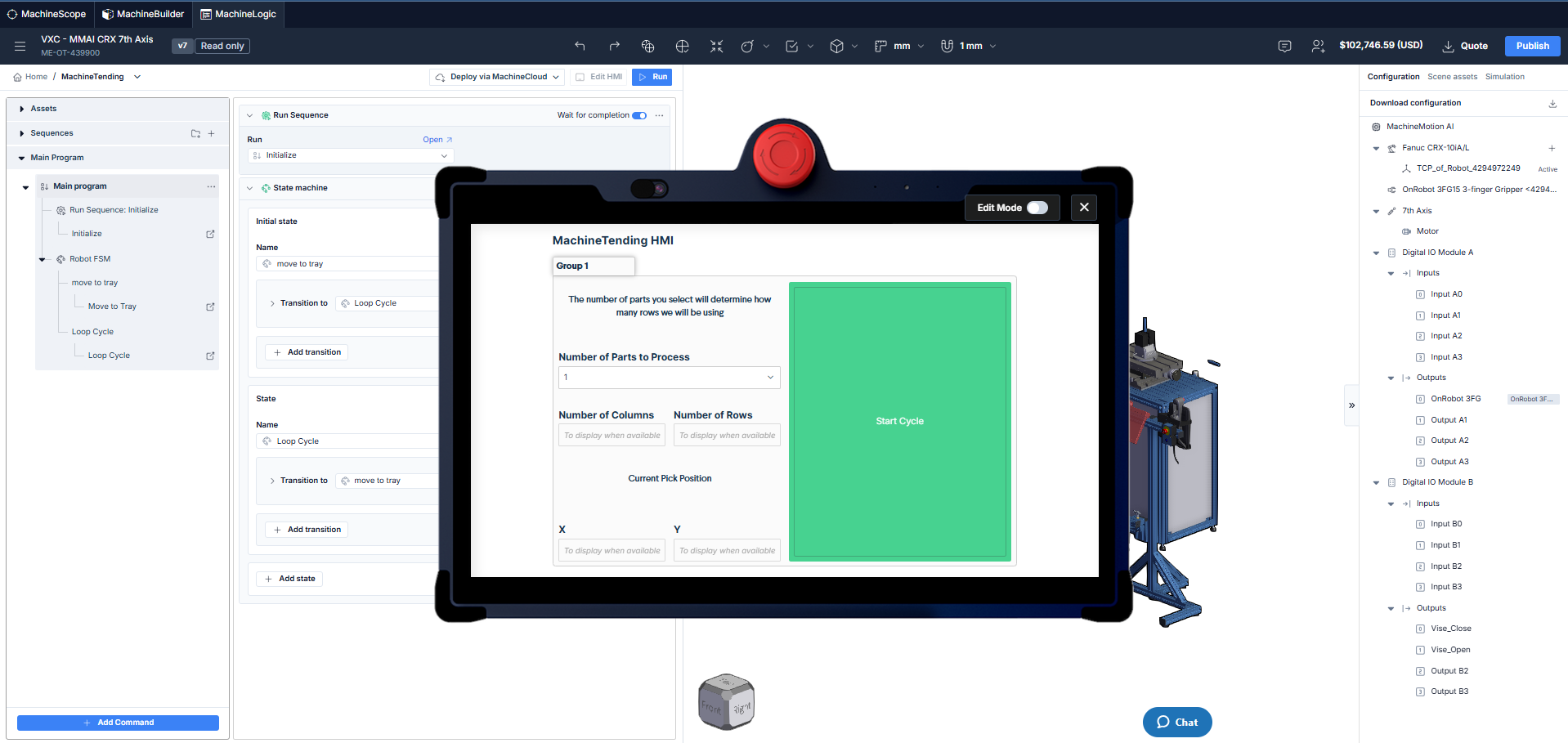
Operator interface created using HMI Builder
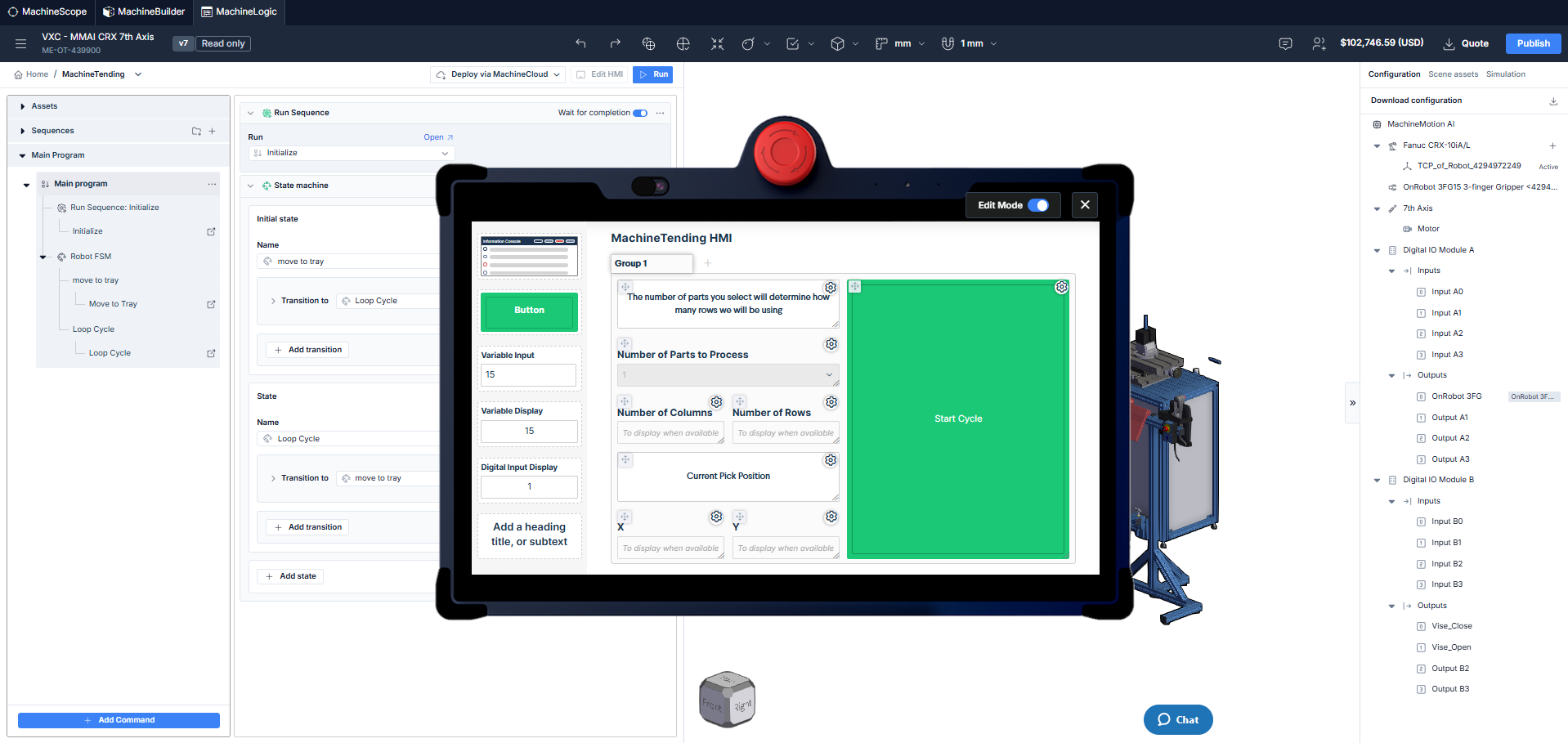
HMI Builder in edit view
The following widgets are available in HMI Builder:
Edit Mode: toggles between edit and play mode. The application can be launched in Play mode.
Group: Allows the creation of additional pages when the plus icon is selected.
Information Console: Shows message in the console when an Add Message command is read,
Button: Sends an MQTT topic that can be used within the application to trigger events.
For more information about Events and MQTT , click here.Variable Input: Sets the value of a variable from the Operator Interface
Variable Display: Displays the current value of a variable.
Digital Input Display: Displays the current state of a digital Input.
Label: Add text to the operator interface
The Variable Input and variable Display widgets are only available in Code-free apps
Integrating HMI Builder in a Code-Free Application
In code-free applications, HMI builder can be used to send MQTT topics and events that can be received by the application. Use the Button widget in conjunction with Wait for MQTT message instruction or configure a State machine transition to fire on the reception of an MQTT topic.
It is also possible to assign an MQTT message to a variable (using the result variable input field) this can be handy when process parameters or communication strings are received from another device present on the network.
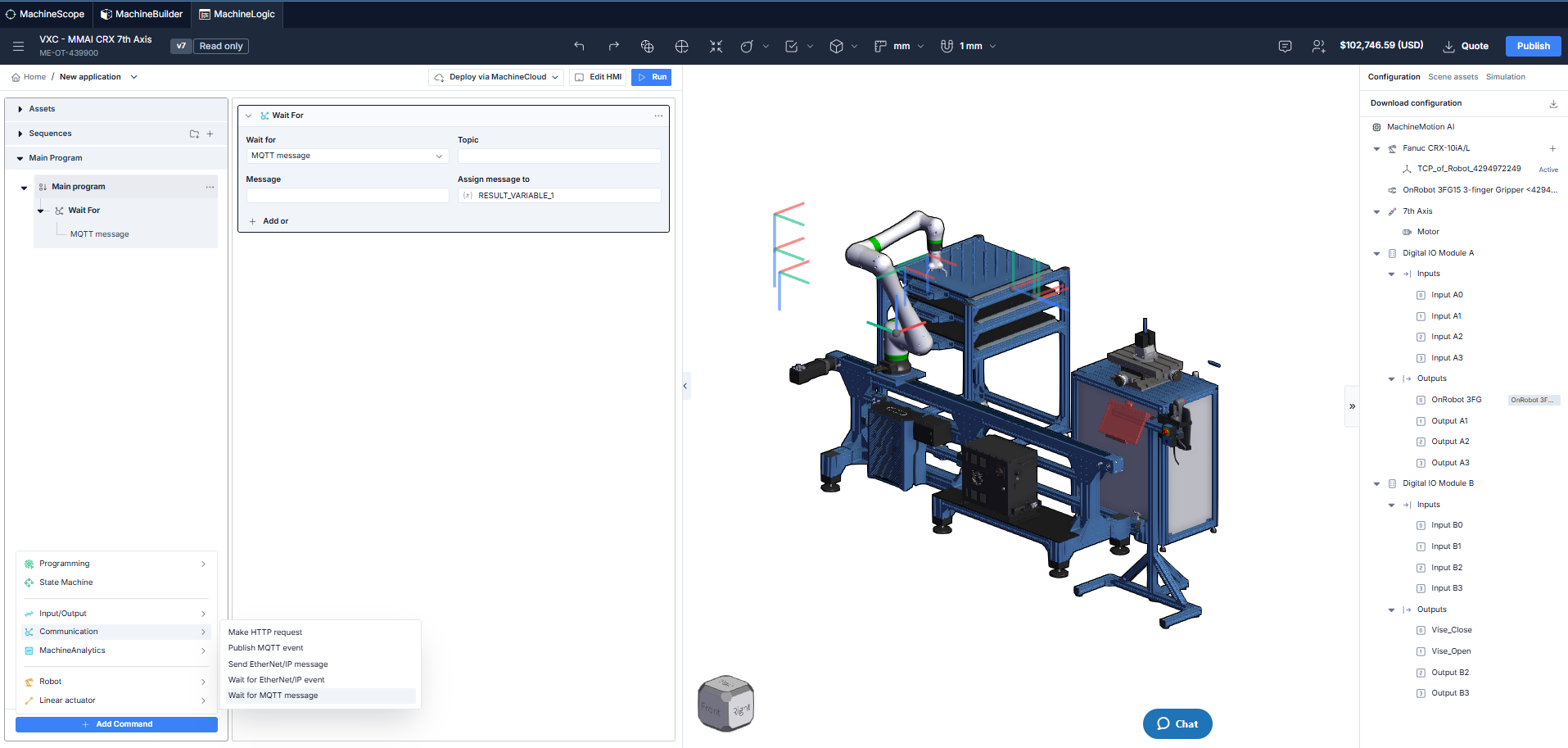
Wait for MQTT Message instruction
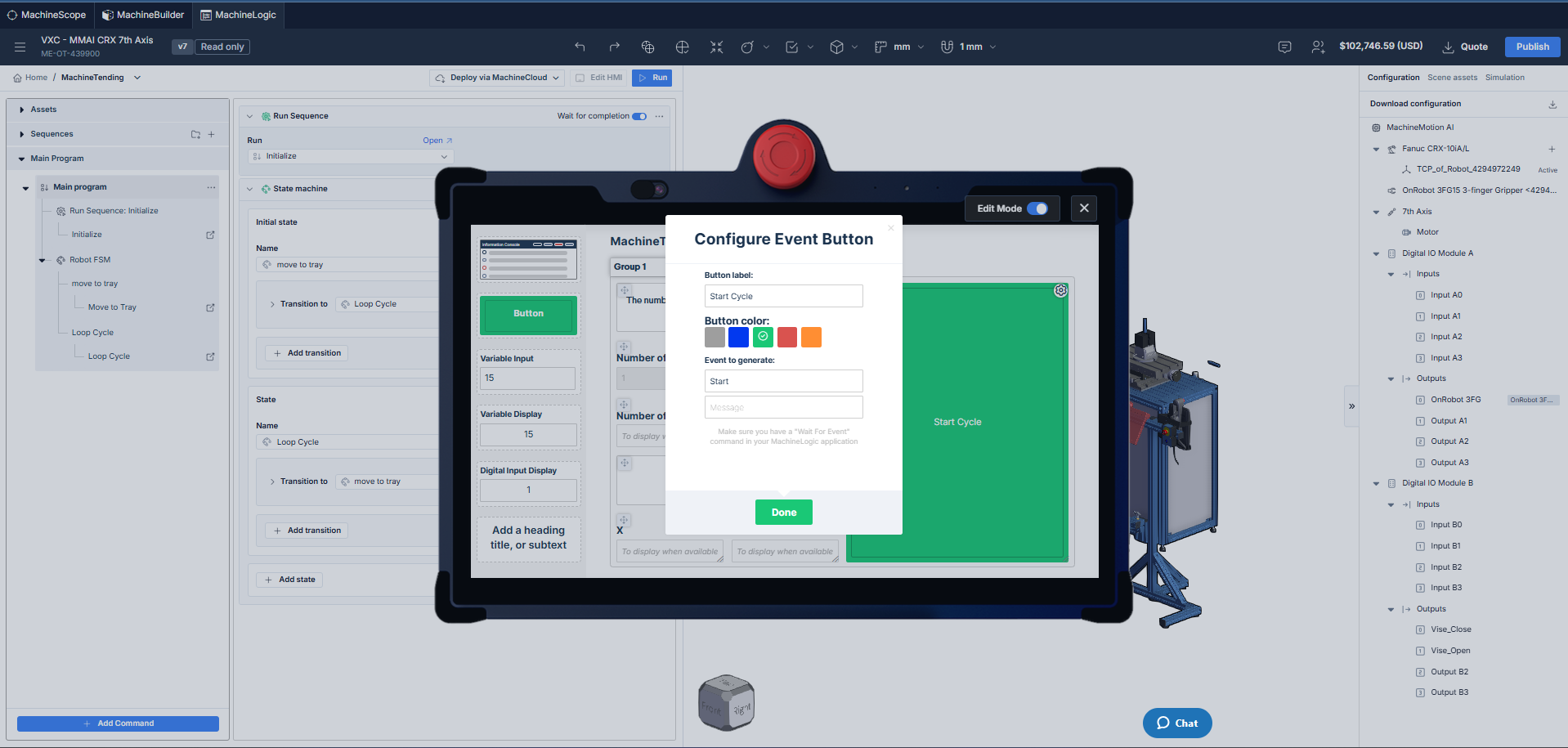
Configurating a button to send an MQTT topic and message
Integrating HMI Builder in a Python Application
HMI builder uses the MQTT protocol to communicate between the automation control code and the Operator interface. To learn more about HMI builder
To link a functionality in the application with an MQTT event outputted by HMI builder, the on_mqtt_event method must be used. Click here for more information.
Here is example for using this method when the “Start” topic is received from the Operator Interface:
# Functions
def Start_Conveyor(topic, message):
my_conveyor.move_continuous_async(250, 1000) # speed of 250 mm/s and acceleration of 1000 mm/s^2
### Program ###
machine.on_mqtt_event('Start', Start_Conveyor) # start event received from operator button pressIn this example, we begin by creating a function containing both a topic and message argument. We then use the machine.on_mqtt_event to link the previously defined function as a callback when the ‘Start’ event is received